ATOMS AND MOLECULES
TlNY PARTICLES CALLED ATOMS are the basic
building blocks that make up everything around
us. Forces called bonds effectively
"cement" the atoms
together. A molecule is a cluster of atoms linked by bonds. There are just over a hundred different types of atom, which are themselves
made up of even smaller "subatomic"
particles, such as protons, neutrons, and
electrons.
|
อะตอมและโมเลกุล
อนุภาคเล็ก ๆ
ที่เรียกว่า อะตอม คือหน่วยโครงสร้างขั้นพื้นฐานที่สร้างทุกสิ่งทุกอย่างรอบ ๆ
ตัวเรา พลังที่เรียกว่า พันธะ ยึดติดอะตอมเข้าด้วยกันอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
โมเลกุลคือกลุ่มของอะตอมที่เชื่อมโยงกันด้วยพันธะ มีอะตอมต่าง ๆ มากกว่าร้อยชนิด
ซึ่งเกิดจากอนุภาคย่อยของอะตอมที่มีขนาดเล็กกว่าด้วยซ้ำ เช่น โปรตอน นิวตรอน
และอิเล็คตรอน
|
|
Atomic structure
The centre, or nucleus,
of an atom contains particles called protons, which
carry a positive electric charge, and neutrons, which carry none. Arranged around the nucleus
in layers called shells are negatively charged particles called electrons. The atom has
no overall charge, because it contains equal numbers of electrons and protons, so the positive and
negative charges are balanced. |
โครงสร้างของอะตอม
ใจกลางหรือนิวเคลียสของอะตอมมีอนุภาคที่เรียกว่า
โปรตอน ซึ่งมีประจุไฟฟ้าเป็นบวก และนิวตรอนซึ่งไม่มีประจุไฟฟ้า อนุภาคที่มีประจุไฟฟ้าเป็นลบ
เรียงอยู่รอบ ๆ นิวเคลียส ในชั้นที่เรียกว่า เปลือก (shell) เรียกว่า อิเล็กตรอน อะตอมไม่มีประจุโดยรวม
เนื่องจากมีจำนวนอิเล็กตรอนและโปรตอนเท่ากัน ดังนั้น
ประจุที่เป็นบวกและเป็นลบจึงสมดุลกัน
|
|
Isotopes
All the atoms of an element
have the same number of protons in the nucleus,
but some atoms, called isotopes, have different numbers
of neutrons. For example, the
carbon isotope carbon-12 has six
protons
and six neutrons,
but the isotope carbon-14 has two
extra neutrons.
|
ไอโซโทป
อะตอมทั้งหมดของธาตุมีจำนวนโปรตรอนในนิวเคลียสเท่ากัน
แต่มีอะตอมบางตัวที่เรียกว่า ไอโซโทป มีจำนวนนิวตรอนแตกต่างกัน ยกตัวอย่างเช่น คาร์บอนไอโซโทป
คาร์บอน-12 มีโปรตอน 6 ตัวและนิวตรอน 6 ตัว แต่ไอโซโทปคาร์บอน-14 มีนิวตรอนพิเศษ 2 ตัว
|
Quarks
Both
neutrons and protons consist of three smaller particles called quarks, stuck together by tiny
particles called gluons. Quarks, in turn, may contain
even
smaller particles.
|
ควาร์ก
ทั้งนิวตรอนและโปรตอนประกอบด้วยอนุภาคเล็ก
ๆ จำนวน 3 ตัว เรียกว่า
ควาร์ก (quark) ซึ่งมีอนุภาค เล็ก ๆ ที่เรียกว่ากลูออน (gluon) ยึดติดไว้ด้วยกัน ในทางกลับกัน ควาร์ก อาจมีอนุภาคขนาดเล็กกว่า |
|||
Electron
shells and valency
Atoms
can have up to seven shells of electrons. An atom with
eight electrons in its outermost shell is very stable. Bonds form when atoms gain, lose, or
share electrons in order to achieve this stable
arrangement. An atom's valency is the number
of bonds it can form with other atoms.
|
เปลือกอะตอมและเวเลนซี
อะตอมมีเปลือกอิเล็กตรอนได้ถึง 7 ชั้น
อะตอมที่มีอิเล็กตรอน 8 ตัวอยู่ในเปลือกชั้นนอกสุดจะมีเสถียรภาพมาก พันธะจะก่อตัวขึ้นเมื่ออะตอมได้รับ
สูญเสียหรือใช้อิเล็กตรอนร่วมกันเพื่อให้ได้รับการจัดเรียงที่มีเสถียรภาพนี้ เวเลนซีของอะตอมคือจำนวนของพันธะที่มันสามารถก่อตัวขึ้นกับอะตอมอื่น
ๆ ได้
|
Ionic
bonds
When
an electron transfers from one atom to
another, the atoms become charged particles called ions. The atom losing the electron becomes a positively
charged ion, and the atom gaining the electron becomes a negatively charged ion. The
force of attraction between the ions opposite charges is
called an ionic bond.
|
พันธะไอออนิก
เมื่ออิเล็กตรอนถ่ายโอนจากอะตอมตัวหนึ่งไปยังอะตอมอีกตัวหนึ่ง
อะตอมจะกลายเป็นอนุภาคที่มีประจุไฟฟ้าที่เรียกว่า ไอออน
อะตอมที่สูญเสียอิเล็กตรอนจะกลายเป็นไอออนที่มีประจุไฟฟ้าเป็นบวกและอะตอมที่ได้รับอิเล็กตรอนจะกลายเป็นไอออนประจุไฟฟ้าเป็นลบ
พลังของแรงดึงดูดระหว่างไอออนตรงข้ามกับประจุไฟฟ้า เรียกว่า พันธะ ไอออนิก
|
||||
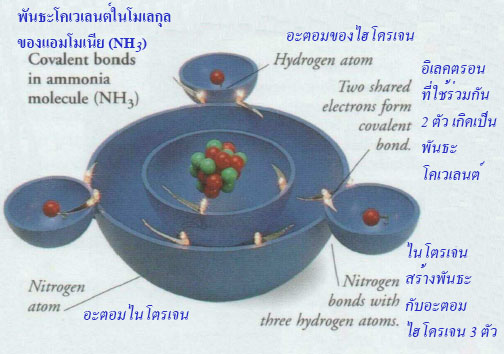
Covalent bonds
A covalent bond
forms when two atoms link up by sharing electrons. Each atom supplies an electron, and the
pair of electrons orbits the nuclei of both atoms, holding the atoms together as a molecule.
|
พันธะโคเวเลนต์
พันธะโคเวเลนต์เกิดขึ้นเมื่ออะตอม 2
ตัวเชื่อมโยงกันด้วยการแบ่งปันอิเล็กตรอน อะตอมแต่ละตัวจะมีอิเล็กตรอนและคู่ของอิเล็กตรอนจะโคจรรอบนิวเคลียสของอะตอมทั้งสองตัวยึดอะตอมเข้าด้วยกันเป็นโมเลกุล
|
|
Double bonds
Sometimes atoms form covalent bonds by sharing two pairs of
electrons. This is called a double
bond. A triple covalent bond forms when atoms share three pairs of
electrons.
|
พันธะคู่
บางครั้งอะตอมจะเกิดพันธะโคเวเลนต์โดยการใช้อิเล็กตรอนสองคู่ร่วมกัน
เช่นนี่เรียกว่า พันธะคู่ พันธะสามเกิดขึ้นเมื่ออะตอมใช้อิเล็กตรอนสามคู่ร่วมกัน
|
Bonds
between molecules
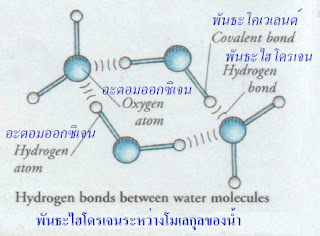
The
molecules of covalent compounds are held together by
weak bonds called Van der Waal's forces. Some
hydrogen-containing compounds, such
as water, have stronger forces called hydrogen bonds between their molecules. In water, these bonds form because each oxygen
atom in a water molecule is attracted to hydrogen atoms
in two nearby molecules.
|
พันธะระหว่างโมเลกุล
โมเลกุลของสารประกอบโคเวเลนต์จะถูกจับเข้าด้วยกันโดยพันธะอ่อนที่เรียกว่า
แรงวานเดอร์วาลส์ (Van der Waals) สารประกอบไฮโดรเจนบางชนิด เช่น น้ำ
จะมีแรงเข้มข้นกว่าที่เรียกว่า พันธะไฮโดรเจนระหว่างโมเลกุลของมัน ในน้ำพันธะเหล่านี้เกิดขึ้นเนื่องจากอะตอมของออกซิเจนแต่ละตัวในโมเลกุลของน้ำถูกดึงดูดเข้ากับอะตอมไฮโดรเจนในโมเลกุลใกล้เคียง
2 ตัว
|
|
Chemical
formula
Scientists use a kind of code called a chemical
formula to describe a substance. The formula uses
letters and numbers to show which elements are present
in the substance, and in what proportions.
Methane, for example, has a chemical formula of
CH4 which shows that it contains carbon (C) and hydrogen (H), combined in the ratio of
one carbon atom to every four
hydrogen atoms.
|
สูตรเคมี
นักวิทยาศาสตร์ใช้รหัสที่เรียกว่า
สูตรเคมี ในการอธิบายสสาร สูตรจะใช้อักษรและตัวเลขเพื่อใช้แทนธาตุในสสาร และในสัดส่วนเท่าใด
ยกตัวอย่าง มีเทนมีสูตรทางเคมีว่า CH4 แสดงว่า มีคาร์บอน (C) และไฮโดรเจน (H) รวมอยู่ในอัตราส่วน อะตอมของคาร์บอน 1 ตัว ต่ออะตอมของไฮโดรเจน 4 ตัว
|
Linus
Pauling
The
American chemist Linus Pauling (1901-94) won the 1954 Nobel Prize for Chemistry
for his work on chemical bonds and the structure of
molecules. He calculated the energies needed to make bonds, the angles at which bonds
form, and the distances between atoms. He also
won the 1962 Nobel Peace Prize for
his efforts to stop the testing of
nuclear weapons.
|
ไลนัส พอลิง
ไลนัส พอลิง นักเคมีชาวอเมริกา (มีชีวิตระหว่าง
ค.ศ. 1901 – 94 = พ.ศ. 2444 – 2537 อายุ 93 ปี) ได้รับรางวัลโนเบล ในปี ค.ศ.
1954 (พ.ศ. 2497) สาขาเคมี จาผลงานด้านพันธะเคมีและโครงสร้างของโมเลกุล เขาคำนวณพลังงานที่จำเป็นในการสร้างพันธะ
มุมที่พันธะเกิด และระยะห่างระหว่างอะตอม เขายังได้รับรางวัลโนเบลสาขาสันติภาพในปี
ค.ศ. 1962 (พ.ศ. 2505) จากความพยายามในการหยุดการทดสอบอาวุธนิวเคลียร์
|
|