Early American
civilizations
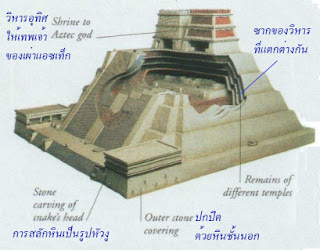
The Aztecs, who
ruled in what is now Mexico from the 14th to 16th
centuries, built stone pyramids to their gods. The remains of five separate temples
have been found at Tenochtitlan, built one on top of the other as new rulers erected bigger temples
on the same site.
|
อารยธรรมอเมริกายุคแรก
เผ่าแอซเท็กผู้ที่ปกครองบริเวณที่เรียกว่า
เม็กซิโก ในปัจจุบัน ตั้งแต่ศตวรรษที่ 14 – 16 ได้สร้างพีระมิดหินอุทิศให้กับเทพเจ้า
ซากของวิหารที่เด่นชัด 5 แห่ง ค้นพบที่เตนอชตีตลัน (Tenochtitlan) ได้สร้างวิหารหลังหนึ่งบนยอดของอีกหลังหนึ่ง
ในขณะที่นักปกครองคนใหม่ก็สร้างวิหารที่ใหญ่กว่าบนสถานที่แห่งเดียวกัน
|
Baroque and
Neoclassical
The Baroque
style emerged in early 17th century Europe. It introduced buildings with ornate decoration, complex shapes, and
dramatic lighting. It was followed by the
Neoclassical style, which revived the more restrained
Classical traditions. This was
partly as a reaction to Baroque excess.
|
สถาปัตยกรรมแบบบาโรกและแบบฟื้นฟูคลาสสิก
รูปแบบบาโรกเกิดขึ้นในยุโรปต้นศตวรรษที่
17 ถูกนำมาใช้กับสิ่งก่อสร้างเพื่อเป็นเครื่องประดับตกแต่งหรูหรา
รูปทรงสลับซับซ้อน และมีแสงสว่างน่าทึ่ง เป็นการทำตามรูปแบบฟื้นฟูคลาสสิก ซึ่งเป็นการฟื้นฟูรูปแบบของยุคคลาสสิกที่มีรูปแบบจำกัดมากกว่า
บางส่วนก็ตอบสนองต่อสถาปัตยกรรมบาโรกมากเกินไป
|
|
The 19th
and 20th centuries
The
development of new, very strong materials made it
possible to construct buildings which were often highly original
in style and owed little to the past. Helped
by better technology, architects turned to glass, steel,
and concrete to express their vision of modern
architecture.
|
สถาปัตยกรรมศตวรรษที่ 19 และ 20
การพัฒนาวัสดุที่ใหม่มีความแข็งแรงมากทำให้มีความเป็นไปได้ที่จะสร้างสิ่งก่อสร้างซึ่งปกติมีรูปแบบเป็นของดั้งเดิมมากและเชื่อว่าเป็นผลมาจากอดีตเพียงเล็กน้อย
ด้วยการช่วยเหลือจากเทคโนโลยีที่ดีกว่า สถาปนิกจึงหันกลับไปหากระจก เหล็ก
และคอนกรีตเพื่ออธิบายวิสัยทัศน์ของพวกเขาที่มีต่อสถาปัตยกรรมสมัยใหม่
|
||||
Interlocked vaults
The dramatic profile
of the Opera House dominates Sydney Harbour. The building's roof of interlocked
vaults, made from reinforced concrete covered with
gleaming tiles, resembles a ship in sail.
|
โครงสร้างทรงโค้งที่เชื่อมต่อกัน
รายละเอียดที่น่าทึ่งของโรงอุปรากร
(Opera
House) ที่มีอิทธิพลเหนืออ่าวซิดนีย์
หลังคาของอาคารมีโครงสร้างทรงโค้งที่เชื่อมต่อกัน ทำจากคอนกรีตที่ทำให้แข็งแกร่งขึ้น
มุงด้วยกระเบื้องอันแพรวพราว คล้ายกับเรือแล่นใบ
|
||||
Skyscrapers
The
invention of the lift during the 19th century made it practical to build skyscraper: and
the first appeared in Chicago, USA, in the 1880s. Today, most are constructed for large businesses: they convey perfectly
an
image
of wealth, size, and strength.
|
ตึกระฟ้า
การประดิษฐ์ลิฟต์ในช่วงศตวรรษที่ 19
ทำให้การสร้างตึกระฟ้าเป็นไปได้จริง และก็เกิดขึ้นเป็นครั้งแรกในนครชิคาโก
สหรัฐอเมริกา ในทศวรรษที่ 1880 ปัจจุบัน
ตึกระฟ้าส่วนใหญ่จะถูกสร้างขึ้นเพื่อธุรกิจขนาดใหญ่ ตึกเหล่านั้นสื่อไปถึงภาพของความมั่งคั่ง
ขนาด และความแข็งแรงอย่างสมบูรณ์
|
|
steel
Following
the arrival of reinforced steel, very tall
structures could be built
for
the first time. An internal steel
skeleton supports the weight of a skyscraper,
such as the 102 storeys of the Empire
State Building.
|
เหล็ก
หลังจากได้เหล็กมาเสริมแรงแล้ว
โครงสร้างที่สูงมาก ๆ ก็ถูกสร้างขึ้นเป็นครั้งแรก โครงสร้างของเหล็กภายในก็รองรับน้ำหนักของอาคารสู้ได้
เช่น ตึกเอ็มไพร์สเตต 102 ชั้น เป็นต้น
|
|
Architects
An architect designs
a building and oversees its construction. Successful
architects become very well-known. Until recently, architects drew large
numbers of plans to
instruct builders and engineers. Much of this work is now carried out on
computer.
|
สถาปนิก
สถาปนิกจะออกแบบอาคารและตรวจสอบโครงสร้างของอาคาร
สถาปนิกผู้ประสบผลสำเร็จจะกลายเป็นผู้มีชื่อเสียงมาก
จนกระทั่งเมื่อเร็ว ๆ นี้
สถาปนิกได้วาดแบบแปลนจำนวนมากมายเพื่อแนะนำช่างก่อสร้างและวิศวกร ปัจจุบันงานแบบนี้มากมายได้ปฏิบัติการด้วยคอมพิวเตอร์
|
|
Le
Corbusier
Le
Corbusier was the name used by the Swiss-French
Charles Edouard Jeanneret (1887-1965), the most influential 20th century architect. Le Corbusier promoted
the use of new materials and construction techniques. His imaginative buildings favoured
plain, often severe, geometric forms.
|
เลอกอร์บูซีเย
เลอกอร์บูซีเยเป็นนามแฝงของ ชาร์ล-เอดูอาร์ จาเนอเร-กรี
ลูกครึ่งสวิสฝรั่งเศส (Charles Edouard Jeanneret มีอายุระหว่าง ค.ศ. 1887 – 1965 = พ.ศ. 2430 –
2508 อายุ 78 ปี) ผู้เป็นสถาปนิกที่มีอิทธิพลมากที่สุดในศตวรรษที่
20 เลอกอร์บูซีเยได้สนับสนุนการใช้วัสดุและเทคนิคการก่อสร้างใหม่ ๆ สิ่งก่อสร้างในจินตนาการของเขานิยมรูปทรงเรขาคณิตที่เรียบง่าย
มีความเข้มงวดเป็นประจำ
|
|
Timeline
|
|
เส้นเวลา
|
|
2650 BC
The Step Pyramid in Egypt is designed.
|
|
2650
ก่อนคริสตกาล พีระมิดขั้นบันไดในอียิปต์ได้รับการออกแบบ
|
|
c.300 BC Buddhist temple mounds appear in India.
|
|
ศตวรรษที่
300 ก่อนคริสตกาล กองหินของวัดในพระพุทธศาสนาปรากฏขึ้นในประเทศอินเดีย
|
|
AD 82
Colosseum built in Rome. Dozens of stone arches support the walls of this stone arena.
|
|
ค.ศ. 82
(พ.ศ. 625) โคลอสเซียมได้รับการก่อสร้างในกรุงโรม ซุ้มโค้งหินหลายโหลรองรับผนังสนามกีฬาหินแห่งนี้ไว้
|
|
690-850 Early Islamic buildings are designed around courtyards.
|
|
ค.ศ. 690
– 850 (พ.ศ. 1233 – 1393) สิ่งก่อสร้างในศาสนาอิสลามยุคแรกได้รับการออกแบบรอบ ๆ
สนาม
|
|
1100-1500 Gothic churches built in Europe.
|
|
ค.ศ.
1100 – 1500 (พ.ศ. 1643 – 2043) โบสถ์แบบกอทิกได้รับการสร้างขึ้นในยุโรป
|
|
c. 1420 Renaissance begins in Italy; architects return to the elegant,
ordered values of Classical builders.
|
|
ศตวรรษที่
1420 สมัยฟื้นฟูศิลปวิทยาเริ่มขึ้นในอิตาลี สถาปนิกหันกลับไปหาคุณค่าของช่างก่อสร้างยุคคลาสสิก
อันงดงาม เป็นระเบียบเรียบร้อย
|
|
19th
century Industrial Revolution: mass-produced materials transform construction.
|
|
ศตวรรษที่
19 การปฏิวัติอุตสาหกรรม วัสดุซึ่งผลิตจำนวนมากเปลี่ยนแปลงการก่อสร้าง
|
|
1920s
International Modernism begins, typified
by glass-and-steel towers
and flatroofed, white houses.
|
|
ทศวรรษที่
1920 แนวคิดสมัยใหม่ระหว่างประเทศเริ่มขึ้น มีหอคอยแก้วและเหล็กและทำเนียบขาวที่มีหลังคาแบนเป็นแบบอย่าง
|
|
1970s
Postmodernism develops. It refers
to past styles, in a humourous way. Strong colours are popular.
|
|
ทศวรรษที่
1970 แนวคิดหลังยุคนวนิยมวิวัฒนาการขึ้น แนวคิดนั้นอ้างถึงรูปแบบที่ผ่านมาในแบบตลกขบขัน
สีที่เข้มเป็นนิยมแพร่หลาย
|
|
1990s
Eco-friendly architecture reflects environmental concerns about energy-saving and recycling.
|
|
ในยุคทศวรรษที่
1990 สถาปัตยกรรมที่เป็นมิตรกับสิ่งแวดล้อมสะท้อนถึงความห่วงใยด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมด้วยการประหยัดพลังงานและการหมุนเวียนนำกลับมาใช้อีก
|