ARCHITECTURE
FROM
A TOWERING SKYSCRAPER to a functional factory,
architecture is the art of planning a building. The word
also refers to the different building styles seen
throughout history. Looking at changes in architecture
tells us about earlier societies: the materials that were available to their builders, the skills mastered by
their engineers, and the social ideals that they wished to express in their public buildings.
|
สถาปัตยกรรม
ตั้งแต่ตึกระฟ้าสูงตระหง่านจนถึงโรงงานสารัตถประโยชน์
สถาปัตยกรรมคือศิลปะในการวางแผนการก่อสร้าง คำว่า สถาปัตยกรรม
ยังหมายถึงระบบการก่อสร้างต่าง ๆ ที่พบอยู่ทั่วไปในประวัติศาสตร์ การพิจารณาดูความเปลี่ยนแปลงในสถาปัตยกรรมก็บอกให้พวกเราทราบถึงสังคมในยุคแรกได้
คือ วัสดุที่ช่างก่อสร้างใช้ ทักษะความเชี่ยวชาญของวิศวกร และแนวความคิดทางสังคมที่พวกเขาปรารถนาจะอธิบายในอาคารสาธารณะ
|
|||
Ornament
Early
in the 20th century, many Western
architects rejected all forms of building ornament. This is rare: most
buildings from other periods and cultures use it extensively, and even a simple building
will usually have some decoration to reflect the taste
of its owner. The ancient Greeks,
for
instance, carved the tops, or capitals, of columns to
dignify their most prestigious buildings. The
distinct decorations were based on styles called orders.
|
การประดับตกแต่ง
ในต้นศตวรรษที่ 20
สถาปนิกชาวตะวันตกจำนวนมากปฏิเสธการประดับตกแต่งอาคารทุกรูปแบบ ข้อนี้เป็นสิ่งที่น่าชมเชย
สิ่งก่อสร้างส่วนใหญ่ที่มาจากยุคและวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ จะใช้การประดับตกแต่งอย่างแพร่หลาย
และแม้การก่อสร้างแบบง่าย ๆ ปกติจะมีการประดับตกแต่งบางอย่างเพื่อสะท้อนถึงรสนิยมของเจ้าของ
ยกตัวอย่างเช่น ชาวกรีกโบราณจะสลักยอดหรือหัวเสาเพื่อทำให้สิ่งก่อสร้างอันเป็นที่เคารพนับถือของพวกเขามีความสง่างาม
การประดับตกแต่งที่เด่นชัดจะตั้งอยู่บนพื้นฐานของรูปแบบที่เรียกว่า order
(แบบ)
| |||
Dome
Domes - curved, solid roofs - were first built
on palaces and religious buildings as striking symbols of the buildings status. They are often difficult to build, and
have been constructed in various shapes: the
Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem is hemispherical; the "onion"-shaped dome is a popular feature of many Russian and
Bavarian buildings.
|
|
หลังคารูปทรงกลม
โคมคือหลังคารูปโค้งทรงตันสร้างขึ้นเป็นครั้งแรกบนสิ่งก่อสร้างในพระราชวังและทางศาสนาเป็นสัญลักษณ์ที่โดดเด่นของสถานะสิ่งก่อสร้าง
ปกติแล้วโดมจะสร้างยากและก่อสร้างรูปทรงต่าง ๆ นานา โดมทองแห่งเยรูซาเลม (Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem) เป็นรูปครึ่งวงกลม
โดมทรงหัวหอมคือรูปแบบอันเป็นที่นิยมทั่วไปของสิ่งก่อสร้างของรัสเซียและบาวาเรีย
(รัฐบาวาเรียในเยอรมนีมีเมืองมิวนิกเป็นเมืองหลวง = แคว้นบาวาเรีย)
|
||
Roof
All
roofs are designed for the practical purpose of providing protection from the weather. The design and covering used will reflect the local climate: for instance, in a wet country a sloping (pitched) roof will
let rain run off. Roofs can also be
ingenious and beautiful, such as when crowning
an ornate castle.
|
หลังคา
หลังคาทั้งหมดได้รับการออกแบบมาเพื่อวัตถุประสงค์ในการป้องกันอากาศ การออกแบบและฝาครอบที่ใช้จะสะท้อนถึงสภาพอากาศในท้องถิ่น ยกตัวอย่างเช่น ในประเทศที่มีอากาศชื้น หลังคาลาดเอียงจะทำให้ฝนไหลออกนอกตัวอาคาร หลังคายังสามารถสร้างให้ยอดเยี่ยมและสวยงามได้ เช่น หลังคาของปราสาทหรูหรา
|
Classical Europe
Classical
architecture is that of the ancient Greeks and Romans. Both built by laying stones on top of
each other, or by resting beams on columns.
The Romans also developed the arch, vault, dome,
and the use of concrete to develop curved spaces.
|
สถาปัตยกรรมยุโรปยุคคลาสสิก
สถาปัตยกรรมยุคคลาสสิกคือยุคของกรีกและโรมันโบราณ
ทั้งสองได้สร้างด้วยการวางหินไว้บนยอดของกันและกันหรือวางคานบนเสา
ชาวโรมันยังพัฒนาช่องโค้งกลม โครงสร้างทรงโค้ง หลังคาทรงกลม
และการใช้คอนกรีตเพื่อพัฒนาพื้นที่โค้ง
|
||||||
|
The Pantheon,
Rome, Italy, completed c. AD 128
|
|||||||
Use
of concrete
Cheap
and durable, this material allowed Roman architects
to cover vast
curved
spaces, which were impossible to
construct before.
|
การใช้คอนกรีต
วัสดุชนิดนี้ราคาถูกและทนทานทำให้สถาปนิกชาวโรมันนำมาปิดพื้นที่โค้งขนาดใหญ่
ซึ่งไม่น่าจะเคยใช้สร้างมาก่อน
|
Symbolism
The Pantheon is a
temple built to all the Roman gods. Light comes through an opening in its
vast dome and moves around the
interior, lighting the curved walls. It
is as if even the Universe turns around
the centre of the
building, symbolizing the power of the
Roman deities.
|
สัญลักษณ์นิยม
วิหารแพนธีอันคือวิหารที่สร้างอุทิศให้กับเทพเจ้าโรมันทุกองค์
แสงจะส่องผ่านช่องในโดมขนาดใหญ่และจะเคลื่อนไปรอบ ๆ ภายใน ส่องผนังโค้ง มันเหมือนกับจักรวาลหมุนรอบศูนย์กลางอาคาร
เป็นสัญลักษณ์แห่งอำนาจของเทพเจ้าโรมัน
|
||||
Gothic
This distinctive,
ornate European style emerged in the 12th century, and was used mainly in cathedrals
and churches. Features include
pointed arches and windows, and elaborate stone tracery used to divide the
openings in window
arches.
สถาปัตยกรรมกอทิก
รูปแบบยุโรปที่โดดเด่น
หรูหรานี้เกิดขึ้นในศตวรรษที่ 12 และถูกนำมาใช้ในวิหารและโบสถ์เป็นส่วนใหญ่ ลักษณะจะมีช่องโค้งและหน้าต่างแหลมและลวดลายหินมีความสวยงามประณีตใช้สำหรับแบ่งช่องในรูปโค้งของหน้าต่าง
|
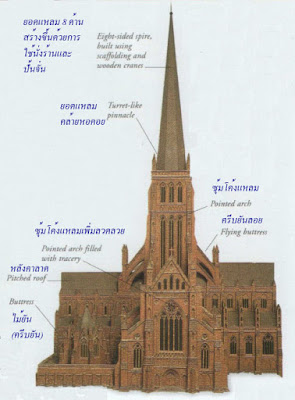
Old St. Paul's Cathedral,
London, England, 1087 – 1666
|
Building innovations
The pointed arch and flying buttress were innovations that
allowed Gothic churches to soar higher
than had been possible before. Pointed
arches can support
heavier, taller structures than round
arches. The flying buttress is a
stone rib which extends down and away
from the walls, transferring weight to the
ground, and giving extra support to a roof or
walls.
การสร้างนวัตกรรม
ซุ้มโค้งแหลมและครีบยันลอยเป็นนวัตกรรมที่ทำให้โบสถ์แบบกอทิกลอยสูงกว่าที่เคยเป็นมาก่อน
ซุ้มโค้งแหลมสามารถรองรับโครงสร้างที่หนักกว่า สูงกว่าซุ้มโค้งมน ครีบยันลอยเป็นโครงหินที่ยื่นออกมาและห่างจากผนังการถ่ายเทน้ำหนักไปที่พื้นและให้การรองรับหลังคาหรือผนังเป็นพิเศษ
|