ATMOSPHERE
LIFE ON
EARTH could not exist without Earth’s atmosphere. The atmosphere is a colourless, tasteless,
odourless blanket of gases that surrounds the Earth. It gives us air to breathe and water to drink. As well as keeping us warm by retaining the Sun's heat, it also shields us from the Sun's harmful rays.
The atmosphere is approximately 700 km (440 miles) deep, but it has no distinct boundary. As it extends into
space, it becomes thinner, eventually fading out. Human activity is upsetting the atmosphere's
natural balance, with damaging results.
|
บรรยากาศ
ชีวิตบนโลกอาจจะดำรงอยู่ไม่ได้หากปราศจากบรรยากาศของโลก
บรรยากาศคือชั้นของก๊าซที่ปราศจากสี ปราศจากรส ปราศจากกลิ่น ที่อยู่รอบ ๆ โลก ให้อากาศสำหรับหายใจและน้ำสำหรับดื่มแก่พวกเรา
อีกทั้งรักษาความอบอุ่นให้กับพวกเราด้วยการป้องกันความร้อนจากดวงอาทิตย์ พร้อมทั้งป้องกันรังสีที่เป็นอันตรายจากดวงอาทิตย์ให้กับพวกเราด้วย
ชั้นบรรยากาศอยู่สูงประมาณ 700 กิโลเมตร (440 ไมล์) แต่ไม่มีขอบเขตที่ชัดเจน เมื่อชั้นบรรยากาศขยายออกไปสู่อวกาศ
ก็มีความเบาบาง ในที่สุดก็ค่อย ๆ หมดไป กิจกรรมของมนุษย์ก็กำลังทำให้เสียความสมดุลทางธรรมชาติ
พร้อมทั้งทำให้เกิดผลเสียหาย
|
|||
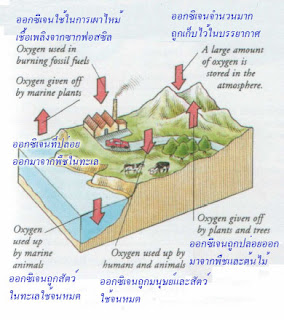
Composition of the atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
is made mainly of two gases — nitrogen
and oxygen. It also contains small amounts of argon and carbon dioxide, with any traces
of other gases. The oxygen is made
primarily by green plants, which maintain the balance of
gases.
|
ส่วนประกอบของบรรยากาศ
บรรยากาศโลกเกิดจากก๊าซหลัก 2 ชนิด
คือ ไนโตรเจนกับออกซิเจน ยังมีอาร์กอนและคาร์บอนไดออกไซด์อยู่จำนวนน้อย อีกทั้งยังมีร่องรอยของก๊าซอื่น
ๆ บ้าง ออกซิเจนส่วนใหญ่เกิดขึ้นจากพืชสีเขียวซึ่งรักษาความสมดุลของก๊าซ
|
|||
Ozone layer
The
thin layer of ozone gas within the stratosphere protects us
by absorbing harmful ultraviolet rays from the Sun. But build-up of man-made
gases called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) has
depleted the ozone layer, and holes have started to
appear in it every spring over the poles.
|
ชั้นโอโซน
ชั้นเบาบางของก๊าซโอโซนภายในชั้นสตราโทสเฟียร์จะป้องกันพวกเราด้วยการดูดซับรังสีอัลตราไวโอเลตที่เป็นอันตรายจากดวงอาทิตย์
แต่การพัฒนาก๊าซที่มนุษย์สร้างขึ้นที่เรียกว่า คลอโรฟลูออโรคาร์บอน (chlorofluorocarbons = CFCs) ทำให้ชั้นโอโซนลดน้อยลงมากและเริ่มปรากฏเป็นช่องโหว่ในชั้นโอโซนเหนือขั้วโลกทุก
ๆ ฤดูใบไม้ผลิ
|
|||
Greenhouse effect
Carbon dioxide and
other gases in the atmosphere act
like glass in a greenhouse, trapping the
Sun's heat. This "greenhouse
effect" keeps the Earth warm. But
human activity, such is burning forests and running cars, releases too much carbon
dioxide into the air and may cause global warming.
|
ปรากฏการณ์เรือนกระจก
คาร์บอนไดออกไซด์และก๊าซอื่น ๆ
ในบรรยากาศ ทำหน้าที่คล้ายกระจกในเรือนกระจก ด้วยการกักความร้อนจากดวงอาทิตย์ “ปรากฏการณ์เรือนกระจก” นี้ ทำให้โลกร้อนขึ้น แต่กิจกรรมของมนุษย์
เช่น การเผาป่าและการขับขี่รถยนต์ จะปล่อยคาร์บอนไดออกไซด์ออกมามากเกินไปในอากาศและเป็นสาเหตุทำให้โลกร้อนขึ้น
|
|||
Layers of the atmosphere
The atmosphere is
divided into five different layers. The
composition of gases varies within these layers, as does the temperature which drops in
the troposphere, the lowest layer, and rises in the stratosphere above.
1. Troposphere 2. Stratosphere 3. mesosphere 4. thermosphere 5. Exosphere |
ชั้นของบรรยากาศ
บรรยากาศแบ่งออกเป็นชั้นต่าง
ๆ 5 ชั้น ส่วนประกอบของก๊าซมีความแตกต่างกันภายในชั้นเหล่านี้ ในขณะที่ความร้อนซึ่งกระจายไปในชั้นโทรโพสเฟียร์ซึ่งเป็นชั้นต่ำสุดและสะท้อนขึ้นไปในชั้นสตราโทสเฟียร์
1. โทรโพสเฟียร์ 2. สตราโทสเฟียร์ 3. มีโซสเฟียร์ 4. เทอร์โมสเฟียร์ 5. เอกโซสเฟียร์ |
||||||||
1.
Exosphere is the outer layer of the atmosphere. Here lighter gases drift into space.
|
|||||||||